
Ever wondered why some companies are always chasing skilled software developers while others seem desperate for sales executives or HR managers? That’s the world of IT non-IT staffing. Both types of recruitment are essential in shaping a company’s success, but they focus on different needs, skills, and industries.
Amoha Recruitment Services specializes in linking driven professionals to opportunities that fit their goals. In today’s fast-changing business environment, knowing the difference between IT and non-IT recruitment can help employers hire smarter and help jobseekers find roles that suit their strengths.
This guide breaks down what is IT recruitment, what is non-IT recruitment, the challenges in IT non-IT recruitment, and why both are crucial for the U.S. workforce. Along the way, we’ll explore real statistics, industry trends, and practical advice to make sense of this topic.
What is IT Recruitment?
At its core, IT staffing means hiring professionals who create, manage, or secure technology systems. These are the people who build the apps you use, maintain cloud servers, analyze data, and protect networks from cyber threats.
Key IT Roles in the U.S.
- Software Developers (Front-End, Back-End, Full-Stack)
- Cloud Solutions Architects (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Cybersecurity Specialists
- Data Scientists and Analysts
- DevOps Engineers
- Artificial Intelligence / Machine Learning Engineers
- Network Engineers
These jobs aren’t just in Silicon Valley anymore. IT staffing now spans fintech in New York, healthcare IT in Boston, federal government contracts in Washington D.C., and remote-first startups nationwide.
Stat Insight: The U.S. IT staffing market was worth $253.9 billion in 2025, and it’s projected to grow at a 5.4% CAGR through 2034, reaching nearly $409 billion (Market Research Future).
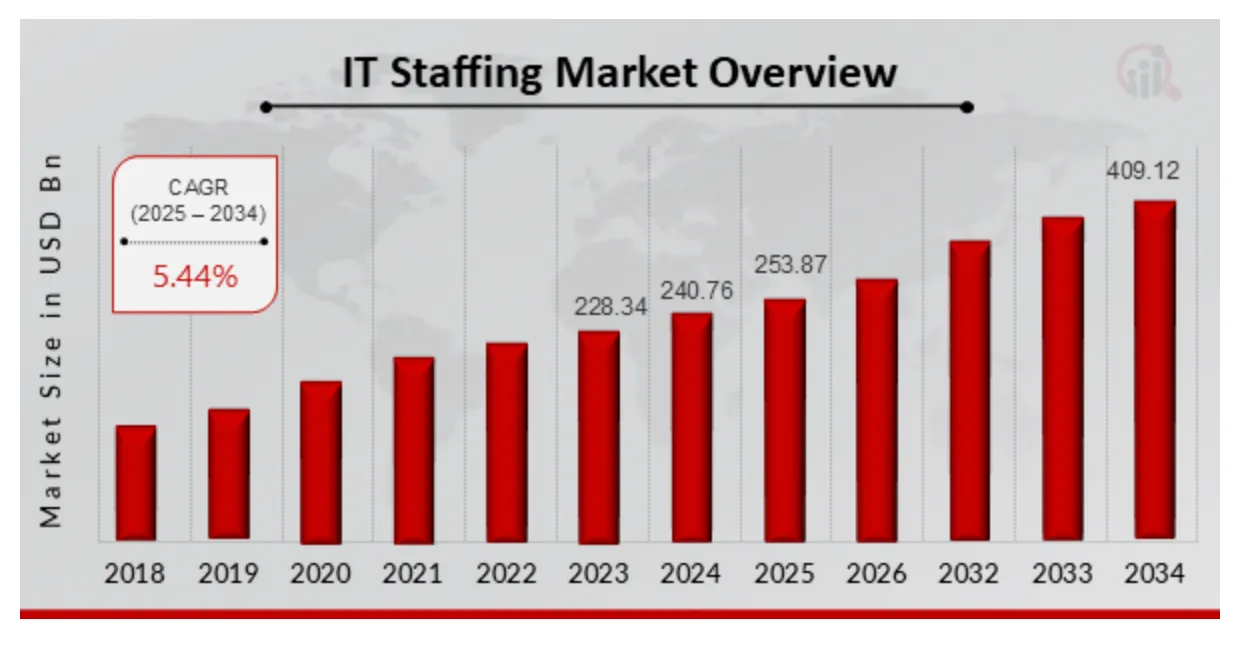
source: Market Research Future
That means businesses are increasingly dependent on IT roles not only to build systems but to stay competitive in digital markets.
What is Non-IT Recruitment?
So, what is non-IT recruitment? In simple terms, it refers to hiring for all roles outside the tech space. These jobs keep the wheels of a business turning, from HR to finance to customer support.
Key Non-IT Professions
- Sales Executives and Business Development Managers
- HR Managers and Talent Acquisition Specialists
- Marketing & Communications Professionals
- Operations and Logistics Coordinators
- Customer Service Representatives
- Accountants and Finance Clerks
- Administrative Staff
Think about a retail chain in Chicago: even if the IT team builds a great e-commerce site, without non-IT professionals like supply chain managers, customer support agents, and sales leads, the business cannot thrive.
Stat Insight: In 2023, the U.S. staffing industry placed 12.7 million temporary and contract employees, with many serving in industrial, clerical, and customer service roles, according to the American Staffing Association (ASA).
Key Differences Between IT and Non-IT Staffing
Let’s break it down in a clear comparison:
| Aspect | IT Staffing | Non IT Staffing |
| Skill Set | Coding, cloud computing, AI, cybersecurity | Communication, sales, HR, operations, customer management |
| Hiring Process | Technical tests, coding interviews, portfolio reviews | Behavioral interviews, situational judgment, past experience |
| Upskilling Need | High – constant training due to rapid tech evolution | Moderate – steady, industry-specific upskilling |
| Market Growth | $253.9B in 2025, 5.4% CAGR (IT staffing market) | Largest share of volume hiring in U.S. industries |
| Recruitment Challenges | Skill shortages, retention, salary competition | High-volume hiring, employee turnover in frontline roles |
| Career Path | Engineer → Lead Developer → Architect → CTO | Executive → Manager → Director/VP → C-Suite |
Both streams require specialized recruitment strategies, but the demands, expectations, and growth paths are very different.
Why Do U.S. Companies Need Both?
Imagine a healthcare company in Dallas:
- Its IT staff manages electronic health records, builds secure patient portals, and ensures compliance with HIPAA cybersecurity regulations.
- Its non-IT staff handles billing, patient support, human resources, and marketing outreach.
Both teams are essential. One without the other would cripple operations. That’s why IT and non-IT staffing has become a must-have rather than an option.
At Amoha Recruitment Services, we help employers balance these needs, ensuring businesses don’t overinvest in one side while neglecting the other.
How Staffing Firms Support IT and Non-IT Hiring?
In the United States, staffing agencies play a crucial role in connecting professionals with the right opportunities. They not only help companies reduce hiring time but also ensure candidates are well-matched to job requirements.
- IT Staffing Firms: Evaluate technical talent through coding tests, portfolio reviews, and skill-based assessments to ensure candidates meet specialized needs in areas like cybersecurity, cloud, or software development.
- Non-IT Staffing Firms: Prioritize adaptability, communication, and cultural fit; key traits that drive success in roles such as customer service, healthcare, retail, or management.
Stat Insight: According to doit.software, the U.S. staffing industry earned $159.1 billion in 2023 and is forecasted to reach $198 billion by 2025, reflecting the critical role of staffing firms in the labor market.”
Beyond recruitment, specialized services like Core Staffing Services, Medical Billing, and Professional Resume Writing provide additional value by helping employers streamline workforce management and empowering jobseekers to stand out in competitive markets.
Challenges in IT Non-IT Recruitment
Recruiting talent in the U.S. isn’t simple. Employers face multiple obstacles:
1. Skill Shortages in IT
- A CompTIA survey reported 77% of employers find it difficult to hire skilled IT talent in areas like cybersecurity and cloud.
- Global labor shortages may result in 85 million unfilled jobs by 2030, many within the IT sector.
2. High Turnover in Non-IT Professions
- Call centers and retail staff see annual turnover rates as high as 30–45% (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics).
- Employers must constantly rehire, retrain, and re-onboard staff.
3. The Rise of Gig Work
- Nearly 40% of U.S. workers are now in gig or contingent roles (One Technology Services).
- This creates flexibility but complicates retention strategies.
4. AI & Automation Pressure
- While automation boosts efficiency, only 7% of U.S. companies currently use AI in recruitment (arXiv).
- As a result, there is a disconnect between possible efficiency and actual implementation.
Future Outlook for Staffing in the U.S.
The staffing landscape in the United States is rapidly evolving, with both IT and non-IT staffing facing new opportunities and challenges. Businesses must adjust to changing employee expectations and advancing technologies to maintain their edge.
IT Staffing Trends
- Cybersecurity & Data Privacy: Rising cyber threats mean a higher demand for skilled security professionals.
- AI/ML Roles: Artificial intelligence and data-driven decision-making are driving new IT recruitment priorities.
- Remote-First Hiring: Flexibility is now expected, with global firms competing for the same U.S. talent.
Non-IT Staffing Trends
- Customer Experience Focus: Businesses are investing more in roles that directly improve customer satisfaction.
- Hybrid Positions: Traditional roles increasingly blend with digital skills, such as sales plus data analytics.
- Agency Support: Firms rely more on staffing agencies for large-scale hiring and workforce flexibility.
The Gig Economy Impact
According to McKinsey, nearly 50% of the U.S. workforce will participate in gig or freelance work by 2030, reshaping how employers balance permanent staff with contract workers. This shift will require staffing firms to adopt more flexible recruitment strategies.
Conclusion
The U.S. economy relies equally on IT and non-IT staffing. While IT professionals build and secure digital systems, non-IT professionals ensure operations, customer service, and growth.
For employers, success means investing in both. For jobseekers, the choice comes down to personal strengths: technical specialization v/s leadership, communication, or customer-facing skills.
We at Amoha Recruitment Services work with individuals and organizations to overcome this gap. Whether you’re exploring opportunities in IT or non-IT recruitment or need support through Core Staffing Services, Medical Billing, or Professional resume writing, we connect the right people with the right roles.
Because when great talent meets the right opportunity, businesses grow; and careers flourish.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is IT staffing only for tech companies?
No. While tech firms dominate IT hiring, industries like banking, healthcare, education, and government also depend heavily on IT teams for cybersecurity, digital platforms, and infrastructure. IT staffing is now essential across almost every U.S. sector.
Which is harder: IT or non-IT hiring?
IT hiring is tough due to limited skilled candidates in areas like cloud computing and cybersecurity. Non-IT hiring becomes difficult when companies must quickly fill large volumes of roles, such as retail or logistics seasonal staffing. Both demand different strategies.
Can one recruiter handle both IT and non-IT?
It’s possible, but specialization matters. IT recruiters evaluate technical skills like coding and systems knowledge, while non-IT recruiters emphasize leadership, communication, and cultural fit. Many staffing firms divide recruiters by expertise to improve accuracy and placement speed.
Which pays more, IT or non-IT?
Entry-level IT jobs usually pay more than entry-level non-IT roles. However, senior-level non-IT positions, such as Vice Presidents of Sales or Finance executives, can equal or surpass IT leadership salaries depending on company size, performance incentives, and industry demand.
What extra services can staffing firms provide?
Beyond hiring, agencies offer services like Core Staffing Services, Medical Billing, and Professional Resume Writing. These services help employers streamline workforce management and assist job seekers in standing out, ensuring smoother recruitment processes and better long-term career growth.
How important are soft skills in IT?
Extremely. Technical ability alone isn’t enough; IT professionals must communicate solutions, collaborate with cross-functional teams, and adapt to changing project needs. In the U.S., employers value teamwork, problem-solving, and adaptability just as much as technical expertise.
Will AI replace recruiters?
No. AI helps recruiters by screening resumes and matching job descriptions, but human insight is critical for assessing cultural fit, motivation, and long-term potential. The future of staffing combines AI efficiency with human empathy and decision-making.

